[this post is under frequent updating]
Retinotopy analysis consists two parts, one on high resolution structural images (segmentation, inflation, cut, etc), the other on functional images.
structural
Before you start, you need to put the structural images into certain directory hierarchy and set environment variable. Assume folder “structural” is where subjects’ structural images are. Under “structural”, you have folders “SUBJ1”, “SUBJ2”, “CON14” etc for every subject. You will have to put your structural images to “structural/SUBJ1/mri/orig/001.mgz”. If you have multiple images for this subject, use “002.mgz” etc. (If you original file format is not mgz, check out how to convert image formats).
structural
|--SUBJ1
|--mri
|--orig
|--001.mgz
|--002.mgz
Then set environment variable in linux shell:
setenv SUBJECTS_DIR $PWD
- Run command recon-all
recon-all -all -subjid CON14
to process structural image. This will run for a long time (30 hours). To see what steps are being done, checkout recon-all manual. - Cut occiput surface
Run command
tksurfer CON14 lh inflated
to display the inflated left hemisphere.
Rotate the brain until the medial surface is facing you.
Then select points along calcarine fissure and press button “Cut line”.
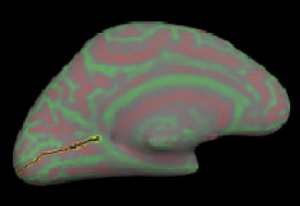
Select 3 points to define the cutting plane: 2 on medial side and 1 on lateral side. Choose a 4th point to specify which portion of surface to keep and press button “Cut plane”.

Save (File > Patch > Save As) as file lh.occip.patch.3d.
(To know how to cut full brain, check out this PDF) - Flatten occiput surface
cd to the subject’s “surf” directory and run
mris_flatten -w 0 -distances 20 7 lh.occip.patch.3d lh.occip.patch.flat
To visualize the patch, you can first load the subject’s inflated surface, then File > Patch > Load Patch …
Flattening takes 1-2 hours. - Repeat step 2 and 3 for the right hemisphere.
functional
- Create directory hierarchy
Create directory “retinotopy”, then under this folder, create directories SUBJ01, SUBJ02, SUBJ03, CON14 etc. Each of these directories is for a subject. Under each subject’s directory, create folder “bold”. In “bold”, create folder “001”, “002” etc, they are folders for runs of a single subject. Note, the name of run folders has to be 3-digit with padding 0s. Something like “01” or “1” won’t work. Under run folders, put the functional imaging data “f.nii” and paradigm file (rtopy.par) there. If your functional image is not a nii file, check out how to convert functional images to Nifti format.Under SUBJ01, create a file called “subjectname” with one line string “SUBJ1” — assuming “SUBJ1” is this subject’s name under “structural” folder. This file is to link this subject’s functional and structural data.
Create file sessid under retinotopy. In this file each line is the folder’s name for each subject.
retinotopy |--sessid |--SUBJ01 |--subjectname |--bold |--001 |--f.nii |--rtopy.par |--002 |--f.nii |--rtopy.parPlease refer to freesurfer’s wiki for detailed explanation. And the following diagram is very helpful:

In rtopy.par file, write two lines
stimtype eccen
direction pos
or
stimtype polar
direction neg - Stay in folder “retinotopy”
- Create analysis
Run the following command
mkanalysis-sess.new -a rtopy -TR 2 -designtype retinotopy -paradigm rtopy.par -funcstem fmcsm5 -ncycles 8Note: ncycles is the number of periods in each run of either ecc or mm. For example, if you have 10 steps going from a small circle to a big circle in ecc, and repeat this for 4 times, then ncycles=4.
After running this program, you will find a directory “rtopy” newly created. There you find two files, analysis.cfg and analysis.info. You may want to change some values there for your own data (e.g. -nskip). If you already removed the extra images, you don’t need to specify -nskip. - Preprocess functional data
Run command
preproc-sess -sf sessid -fwhm 5
or
preproc-sess -s SUBJ01 -fwhm 5
It takes about 40s for one run. (For xc only: you should run this command on scuttlebutt, not rumor) - Register against structural images
Before and after registration, you may use tkregister-sess to view how well the functional images are aligned with structural images.
tkregister-sess -sf sessid -regheader
Green lines are the cortical surface. Hit button “compare” to see the alignment.
To run registration, run command
fslregister-sess -sf sessid - Run the analysis
sfa-sess -a rtopy -sf sessid
(for xc: use scuttlebutt. It takes ~2min) - View intermediate results
sliceview-sess -sf sessid -a rtopy -c eccen -map h -slice mos
sliceview-sess -sf sessid -a rtopy -c polar -map h -slice mos - Run paint
paint-sess -a rtopy -sf sessid
It takes ~1min. - View final result
surf-sess -sf sessid -a rtopy -retinotopy fieldsign -flat
surf-sess -sf sessid -a rtopy -retinotopy eccen -flat
surf-sess -sf sessid -a rtopy -retinotopy polar -flat
surf-sess -sf sessid -a rtopy -c polar -flat
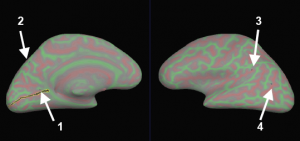
I’v got a problem about the image displayed as the final result in step 9.
After run ‘surf-sess -sf sessid -a rtopy -retinotopy eccen -flat’or ‘surf-sess -sf sessid -a rtopy -retinotopy polar -flat’, i got a image with color scales, But i don’t know what does it mean by the cold blue or the warm red. Can you give me a clue about it.
Thanks ~!